Last Updated on August 3, 2021 by
Lichens are plants without roots, leaves, or flowers. Even though they have no leaves or flowers, they can be quite attractive and range from a pale grey or whitish colour to bright green when they are moist.
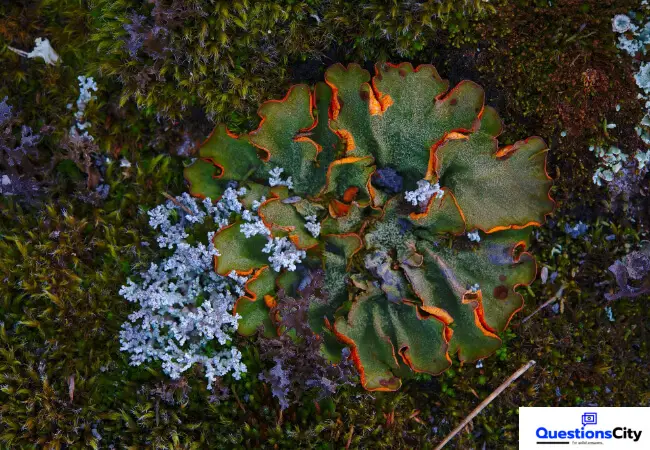

There are about 16,000 species of lichens, and they are found in every conceivable kind of place. They grow in sun-baked deserts and on exposed Antarctic rocks. They grow in waste places, on bare rocks, bare soil, dead wood, and tree bark, and can live through heat, cold, dampness, or dryness. About the only place where they do not thrive is near a city, where they are killed by smoke, dust, and coal gas!
Lichens are really two plants growing together—a “fungus” and an “alga”. The greater part of a lichen plant is greyish, thread-like fungus material. Held among the fungus fibers are bright green cells of algae.
Algae, being green plants, can make their own food, but the non-green fungi cannot. Lichen fungi use food made by the algae. The algae use water absorbed by the fungus, which also shelters and support the algae. Such a relationship where each member benefits from the other are called “symbiosis”, from Greek words meaning “life together”.
Lichens grow very slowly but live a long time. Some colonies are thought to have lived as long as 2,000 years! In some lichens, the fungus produces spores. But most lichens are reproduced by broken-off bits blown or carried to new places, or by special structures that break off easily and become new lichen plants.
Lichens are the first plants to grow on bare rocks. They loosen rock particles, and these particles plus decaying lichens form the first thin layer of soil on which other plants can grow.
Where are lichens found?
Lichens are fascinating plant-like organisms found all over the world. They have a symbiotic relationship with soil bacteria, which give them their unique greenish, reddish, or brown color. The bacteria live in a hollow space that’s created inside the lichen’s leaf-like structure, and they use this space to grow and thrive. Lichens contribute to the stability of the soil, help prevent erosion, improve water filtration, limit plant competition, and maintain the structure of the soil.
How do you identify a lichen?
Lichen is an interesting symbiosis between two organisms. One organism is a photosynthesizing plant or fungus, while the other is an animal or fungus that lives on the surface of the plant or fungus. This symbiosis is called “lichenization” and it is a well-studied biological phenomenon. The symbiotic relationship is not always beneficial to the organisms living in it and can have negative impacts on the host. Lichens are found all around the world and are cosmopolitan in distribution. They can be found on every continent except Antarctica and most islands.
What is lichen used for?
Lichen is a common plant that naturally grows on trees and rocks. Most people take lichen for granted, but in fact, many people are interested in this natural material. Lichen is used as a natural building material, as well as an ingredient in cosmetics and medicine.
What Are The 3 Types Of Lichens?
There are three main types of lichens: Foliose. Fruticose. Crustose.
What is a lichen Class 7?
Lichens are earth’s first ecosystem. They’re symbiotic organisms with algae in their cells and fungal cells in their tissues. They’re the oldest living things on earth. They do not need sunlight to grow, yet they can still “breathe”, thanks to symbiotic algae. While they do not have chlorophyll, they still perform photosynthesis. Lichens are the only organisms that can do this. They can photosynthesize when they are wet or dry.