Last Updated on March 19, 2022 by QCity Editorial Stuff
Mitosis and binary fission are two different types of cell division that occur to produce new cells. Mitosis is the process of dividing a single nucleus into two identical nuclei. Binary fission, on the other hand, does not require a nucleus; it simply divides the cytoplasm evenly between each daughter cell.
Mitosis can be seen as more stable than binary fission because mitotic errors like crossing over during meiosis do not happen with mitotic chromosomes. This also means that there is no genetic diversity within an organism’s population, which may lead to problems such as inbreeding depression or loss of immune defenses against foreign antigens.
Comparison between Mitosis and Binary Fission
| Parameters of Comparison | Mitosis | Binary Fission |
| Process | Mitosis is the process of cell division in which one parent cell divides into two daughter cells, | Binary fission is a form of asexual reproduction that involves just one parent cell dividing to produce two identical offspring cells. |
| Phase | Mitosis has four phases – prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. | The first phase in binary fission is called “restriction” where the DNA strands are cut at specific points by enzymes so that replication can take place. |
| Take place | Mitosis takes place in both animal and plant cells, | binary fission only occurs in bacteria |
| Chromosome | In mitosis, each chromosome divides equally between the new cells | but in binary fission, chromosomes are not divided evenly. |
What is Mitosis?
Mitosis is the process of cell division in which one cell becomes two identical cells. Cell division occurs during the development, growth, and repair of tissues. It also occurs when an organism reproduces through sexual or asexual reproduction. Mitosis is essential for the growth and development that allows us to develop into adults with all our organs functioning properly.
Mitosis happens when DNA replicates itself in preparation for cellular division. The replicated chromosomes are then divided between two new daughter cells by wrapping themselves around each other like thread on a spool until they touch at their centromeres (the middle portions). Once they touch, the nuclear envelope breaks down and the nuclear material spills out into both newly created cells along with cytoplasm from both original cells. The replicated chromosomes are now two identical pairs, but they don’t exactly match up since they were replicating from different starting points.
What is Binary Fission?
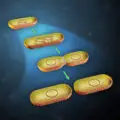
Binary Fission is a process by which cells divide and the two new cells contain half of the original cell’s chromosomes. The process can also occur to produce identical twin organisms or cause tumor growth. Cells undergoing binary fission will duplicate their cytoplasm, nucleoid, and nuclear envelope before dividing into two daughter cells. One of these daughter cells will inherit almost all of the cytoplasm while the other inherits very little, but both get an equal share of organelles such as mitochondria and ribosomes.

10 Differences Between Mitosis and Binary Fission
1. Mitosis is the process of cell division in which one parent cell divides into two daughter cells, each with the same number and kind of chromosomes as the original parent cell.
2. Binary fission is a form of asexual reproduction that involves just one parent cell dividing to produce two identical offspring cells.
3. Mitosis has four phases – prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
4. The first phase in binary fission is called “restriction” where the DNA strands are cut at specific points by enzymes so that replication can take place.
5. In mitosis there are two types of spindle fibers – microtubules and actin filaments.
6. There are three types of spindle fibers during binary fission- microtubules only, actin filaments only, or both.
7. Mitosis takes place in both animal and plant cells, while binary fission only occurs in bacteria.
8. In mitosis, each chromosome divides equally between the new cells, but in binary fission, chromosomes are not divided evenly.
9. Cell size also differs – during mitotic division, daughter cells are about half as large as their parents; whereas with binary fission the offspring are usually smaller than their parents.
10. The result is different too – when dividing through mitosis, there may be leftover portions of cytoplasm called “mitotic figures” or “chromatid fragments”; however sometimes there can be leftover parts after binary fission too.
Interesting Statistics or Facts of Mitosis
1. Mitosis is the process of cell division in living organisms.
2. The word “Mitosis” comes from the Greek words μίτος (mitos) meaning thread and εἶσις (isis) meaning a state of being.
3. Mitosis occurs in most cells, with exceptions including red blood cells and neurons.
4. A mitotic cycle can take place without cytokinesis or one can happen after cytokinesis depending on the need for more space within the cell to divide into new cells.
5. Cytokinesis is known as a cellular division that separates two daughter cells at their end of the mitotic cycle.
6. There are four stages of mitosis – prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Interesting Statistics or Facts of Binary Fission
1. Binary fission is the process of a single cell dividing into two.
2. The resulting cells are genetically identical to each other and the original cell.
3. It’s also called mitosis because it happens in most animal and plant cells.
4. One type of binary fission is sexual reproduction, which is what humans do when they reproduce with another human.
5. For this form of binary fission to work, there need to be two different types of cells that merge.
6. After merging, one set becomes eggs and sperm while the other set becomes an embryo.
Conclusion
Mitosis is a type of cell division that occurs when cells divide to create new daughter cells with the same number and kind of chromosomes as their parent cell. The mitotic division produces two identical daughter nuclei, which develop into two genetically identical cells. In contrast, binary fission is a process by which single-celled organisms reproduce through fragmentation or budding from existing multicellular structures. Unlike mitosis, it does not involve any true cellular division; rather, only one individual becomes two individuals via an increase in size due to continual replication of its genetic material until it reaches reproductive maturity and splits off on its own. Binary Fission can be observed in some microbes such as bacteria and protozoa like amoebae where they grow and divide rapidly.
References:
Resource 01: https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Mitosis
Resource 02: https://micro.cornell.edu/research/epulopiscium/binary-fission-and-other-forms-reproduction-bacteria/