Last Updated on May 1, 2023 by QCity Editorial Stuff
The average person can hold their breath for about 30 seconds to 1 minute. However, this can vary greatly depending on a number of factors, such as age, physical fitness, lung capacity, etc.
How Long Can the Average Person Hold Their Breath?
The answer varies depending on several factors, such as age, gender, and fitness level. On average, a healthy adult can hold their breath for around 30 to 45 seconds. However, some people can hold their breath for much longer.
World Record for Breath-Holding
If you think holding your breath for 30-45 seconds is impressive, wait until you hear about the world record. The current Guinness World Record for breath-holding is a staggering 24 minutes and 3 seconds. This record was set by Aleix Segura Vendrell, a Spanish free diver, in 2016. It’s worth noting, however, that Vendrell had spent years training his body to hold his breath for extended periods before attempting the record.
Physiology of Breathing
Breathing, also known as ventilation, is the process by which the body takes in oxygen and eliminates carbon dioxide. This process is essential for the body’s metabolic processes, which require a constant supply of oxygen to function properly.
The physiology of breathing involves several organs and systems working together. The respiratory system is responsible for the intake of air into the body and the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs. The circulatory system then transports oxygen to the body’s tissues and removes carbon dioxide.
- Anatomy of the Respiratory System
The respiratory system consists of several organs, including the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. Air is taken in through the nose or mouth and passes through the pharynx, which leads to the larynx, or voice box. The larynx then leads to the trachea, or windpipe, which is divided into two bronchi, one leading to each lung. The bronchi divide into smaller bronchioles, which lead to tiny air sacs called alveoli. It is in the alveoli where gas exchange occurs.
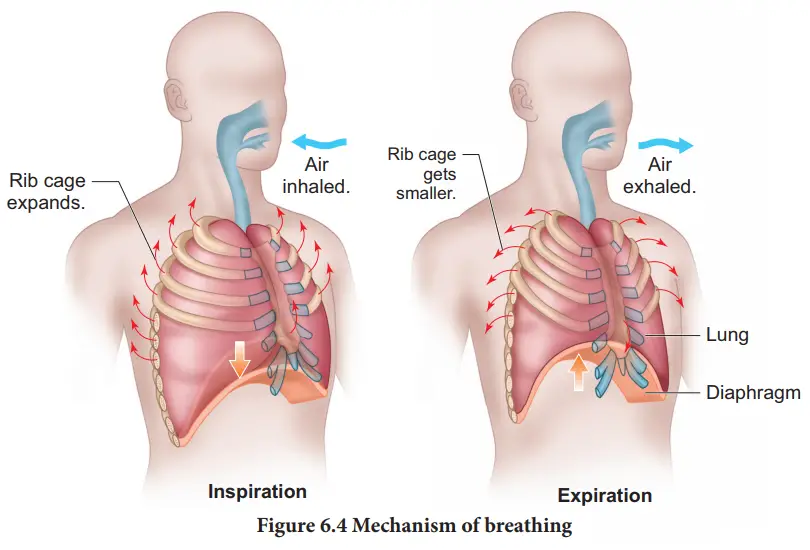
- Mechanism of Breathing
Breathing is controlled by the respiratory center in the brainstem. The process of breathing involves two main phases: inhalation and exhalation. During inhalation, the diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract, causing the chest cavity to expand. This expansion decreases the pressure in the chest cavity, allowing air to rush in through the airways and into the lungs. During exhalation, the diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax, causing the chest cavity to decrease in size. This increased pressure forces air out of the lungs and out through the airways.
Factors Affecting Breath Holding Time
There are several factors that can affect a person’s ability to hold their breath, including:
- Physical fitness: Individuals who are physically fit and have strong respiratory muscles may be able to hold their breath for longer periods of time compared to those who are less fit.
- Lung capacity: People with larger lung capacity may be able to hold their breath for longer periods of time than those with smaller lung capacity.
- Age: Breath-holding time tends to decrease with age, as lung function and respiratory muscle strength decline.
- Gender: In general, men tend to have greater lung capacity and may be able to hold their breath for longer periods of time than women.
- Altitude: At higher altitudes, the air pressure is lower, and the body requires more oxygen. This can make it more difficult to hold your breath for as long as you would at sea level.
- Smoking: Smoking can damage the lungs and respiratory muscles, reducing lung capacity and the ability to hold your breath.
- Anxiety and stress: Anxiety and stress can affect breathing patterns and make it more difficult to hold your breath for extended periods of time.
- Water temperature: Cold water can cause the body to go into a “cold shock” response, making it more difficult to hold your breath underwater.
- Air quality: Poor air quality, such as in areas with high levels of pollution, can affect lung function and make it more difficult to hold your breath.
Importance of Understanding Breath Holding
Here are some key points on the importance of understanding breath-holding:
- Breath-holding is important for athletes who engage in sports like swimming, diving, and free diving, where the ability to hold one’s breath for extended periods of time is crucial for success.
- Understanding breath-holding can help athletes improve their performance and achieve their goals.
- Knowing how to hold your breath properly and for how long can also help prevent accidents and emergencies, particularly in situations where water is involved.
- Understanding breath-holding can help people prepare for emergency situations, such as escaping from a burning building or being stuck in an enclosed space.
- Breath-holding can be used as a relaxation technique to help manage stress and anxiety.
- Proper breath-holding techniques can also be helpful in managing medical conditions such as asthma, by reducing the likelihood of breathing difficulties and panic attacks.
- Knowing when to avoid breath holding, such as in situations where it can be dangerous, is also important for ensuring safety and preventing injury.
Effects of Breath Holding on the Body
Breath-holding, also known as apnea, can have both positive and negative effects on the body, depending on the duration and context of the breath-holding. Here are some of the effects that breath-holding can have on the body:
- Increased heart rate and blood pressure: Breath-holding can cause a temporary increase in heart rate and blood pressure, as the body works to maintain oxygen levels.
- Decreased oxygen levels: Holding your breath can lead to a decrease in oxygen levels in the body, which can cause symptoms such as dizziness, lightheadedness, and even fainting. Prolonged breath holding can lead to more serious consequences such as hypoxia (lack of oxygen) and even brain damage.
- Increased carbon dioxide levels: When you hold your breath, carbon dioxide levels in the body can increase, which can cause symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and confusion.
- Increased tolerance to CO2: Repeated breath holding can increase the body’s tolerance to carbon dioxide, which may be beneficial for certain activities such as free diving.
- Improved lung function: Regular breath-holding exercises can improve lung function and capacity, as well as increase oxygen utilization efficiency.
- Improved mental focus: Breath holding can be used as a technique to improve mental focus and concentration, as it requires concentration and control of the body’s response to oxygen deprivation.
- Potential risks: Prolonged or underwater breath holding can be dangerous and lead to drowning, hypoxia, and brain damage. It is important to always practice breath-holding safely and under the guidance of a trained professional.
References:
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/how-long-can-the-average-person-hold-their-breath






